If you drive a commercial motor vehicle (CMV), operate a fleet of commercial trucks, or are an owner-operator, ELD compliance is a hot topic these days, and for a good reason. Since 2019, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) has required specific CMVs to install a DOT-compliant electronic logging device in their vehicle.
Whether you’re new to ELD devices or considering an upgrade, you will learn the following in this guide. So, let’s dig in!
What Are ELD Systems?
Electronic logging devices (ELDs) are the hardware that commercial motor vehicle drivers use to record driver and vehicle information in real-time. Most ELD devices connect to the truck’s onboard diagnostics (OBD) port to record important information about the vehicle’s engine, speed, driving hours, whereabouts, mileage, and more.
What Type of Information Does an ELD Device Record?
ELDs are telematic devices. That means they can record and transmit various data across long distances, which is much more efficient and accurate than paper logs. Electronic logging devices can record all types of ‘records of duty statuses’ (RODS) in the elog. That includes but is not limited to the following:
- Hours of Service (HOS): The primary purpose of the ELD mandate (more about this in the following sections) is to record the driving hours of commercial motor vehicle operators. Most CMV operators must adhere to the HOS regulations of the federal government.
- Real-time GPS tracking
- Miles traveled, fuel efficiency, and engine speed
- Engine diagnostics and engine hours
- Hazardous driving behavior, including accidents and hard braking
Why Do Commercial Truck Drivers Use ELD Devices?
For the most part, CMV operators use ELDs to monitor and record an operator’s drivetime via an electronic logbook (i.e., elog) to satisfy the FMCSA’s ELD mandate. While this is the base function of most ELD devices, they can also be used as an essential element of commercial fleet management.
Depending on the type of electronic logging device, they can enhance fleet safety and sustainability, make the fleet more efficient, in addition to other benefits. Besides satisfying the ELD mandate and staying in compliance, owner-operators use ELD Devices in the following ways:
- Truck maintenance
- Complete electronic driver vehicle inspection reports (DVIRs)
- Monitor a CMV driver’s safety via the gyroscope and accelerometer
- Monitor, prevent, and report security issues and enhance loss prevention efforts via geofencing technology.
- Reduce fuel consumption, train drivers to be more efficient (e.g., less idling time), and enable coaching based on real-time data reports.
How Does An Electronic Logging Device Record and Transmit Data?
Most electronic logging devices connect to a truck’s onboard diagnostic (OBD) port by transferring information directly from the engine. That includes fuel consumption, how far the vehicle travels, etc. Most ELD solutions include a GPS tracker that informs fleet managers of the real-time location of the truck. In addition to transferring data to fleet managers, they can transmit data to the Department of Transportation (DOT) during roadside inspections.
How is ELD Device Data Transferred?
ELD data can be transferred with a cellular service data plan or via Bluetooth to the operator’s Android or iOS mobile app so they can efficiently log hours of service. Depending on the ELD provider, it may also be equipped with a built-in WiFi hotspot which can help drivers obtain necessary information like:
- Electronic work orders
- Work emails
- Other mobile apps and productivity resources
How ELD Data is Transmitted to the DOT
Generally, the DOT uses roadside inspections to ensure drivers comply with the ELD mandate and enforce HOS regulations. That means a commercial motor vehicle operator can be stopped by the Motor Carrier Safety Assistance Program (MCSAP) at any time to inspect the driver’s record of duty status for the previous week. This ensures they comply with federal regulations.
An ELD solution must at least support local data transfer via USB with the MCSAP roadside inspector to accomplish this. However, federal laws also allow data transfers via Wireless Web Service (on a secure server) and encrypted email.
For the most part, FMCSA recommends data transfers via Wireless Web Service.
Who Needs an ELD Device?
Most trucking companies and owner-operators are required to install an ELD solution under the federal ELD mandate. However, in rare cases, a trucker or trucking company may not be required to install an electronic logging device. Learn more about who the ELD mandate applies to and ELD mandate exemptions in the sections below.
What is the ELD Mandate?
The ELD mandate (also known as the ELD Rule) came into effect in 2015. However, the FMCSA allowed nearly four years for trucking companies and owner-operators to come into compliance with the new law. The last ELD deadline for compliance was December 16, 2019.
The ELD rule essentially stipulates that long-haul CMV operators who must maintain records of duty status are required to install an ELD. Generally, the FMCSA instituted this rule to assist the DOT with tracking and managing RODS in a simpler, more efficient and accurate method.
Further, the ELD mandate also helps to regulate a driver’s HOS more accurately to ensure they get proper downtime and rest before hitting the road. It’s estimated that the ELD rule is responsible for saving thousands of dollars and lives due to taking sleepy truck drivers off the road.
Generally, an ELD is required for any commercial driver who is required by law to track and maintain RODS. Truck drivers and fleet managers who don’t comply with the rule face potential fines and their trucks being taken off the road.
While most ELDs are used for commercial trucks, other types of vehicles may be required to install an ELD solution as well, including vehicles that commercially transport passengers, construction vehicles, etc.
ELD Mandate Exemptions
Most long-haul commercial motor vehicles are required to install an FMCSA-approved ELD solution. However, there are exceptions to the rule. Generally, ELD mandate exemptions include:
- Short-haul drivers who qualify for the short-haul exemption.
- Drivers who are not mandated to keep Records of Duty Service for eight days or fewer within 30 a day period.
- Drivers who only tow or drive away other vehicles for delivery.
- Fleets comprised entirely of vehicles manufactured pre-2000.
- Specific exemptions for vehicles operating in the agricultural industry.
Other than those who fall under the short-haul exemption, all others exempted from the ELD rule must still maintain Records of Driving Status via paper logs or AOBRDs to adhere to hours of service regulations. Learn more about the latter in the following section.
What’s the Difference Between AOBRDs and ELD Devices?
An Automatic On-board Recording Device (AOBRD) is essentially the predecessor to ELDs. Similar to ELD solutions, AOBRDs record HOS. However, the main difference is that ELDs provide fleet managers and the DOT with much more information in alignment with the FMCSA ELD rule.
For example, an AOBRD records a commercial vehicle’s mileage, dates, and location data, but it does not obtain other essential data like whether the truck is on or off nor engine data. There are plenty more examples of the less-than-robust data AOBRDs record compared to ELD devices.
Aside From FMCSA Compliance, What Are The Benefits of ELDs?
Commercial vehicles that fall under the ELD mandate must install an ELD device. The most obvious benefit of doing so is that commercial drivers can stay in compliance, remain on the road, and continue to deliver their loads. However, in addition to these benefits, there are other advantages to installing an ELD solution. They include but are not limited to:
- Less paperwork and administrative duties for fleet managers
- More efficient vehicle dispatch
- Safer driving
- More fuel-efficient commercial vehicles
- Less administrative work for drivers in comparison to paper logs
- Accident logging which can help indemnify drivers from collision liability when they weren’t at fault for the accident
- A leg up on competitors who don’t utilize ELD systems
Which is the Best ELD to Use?
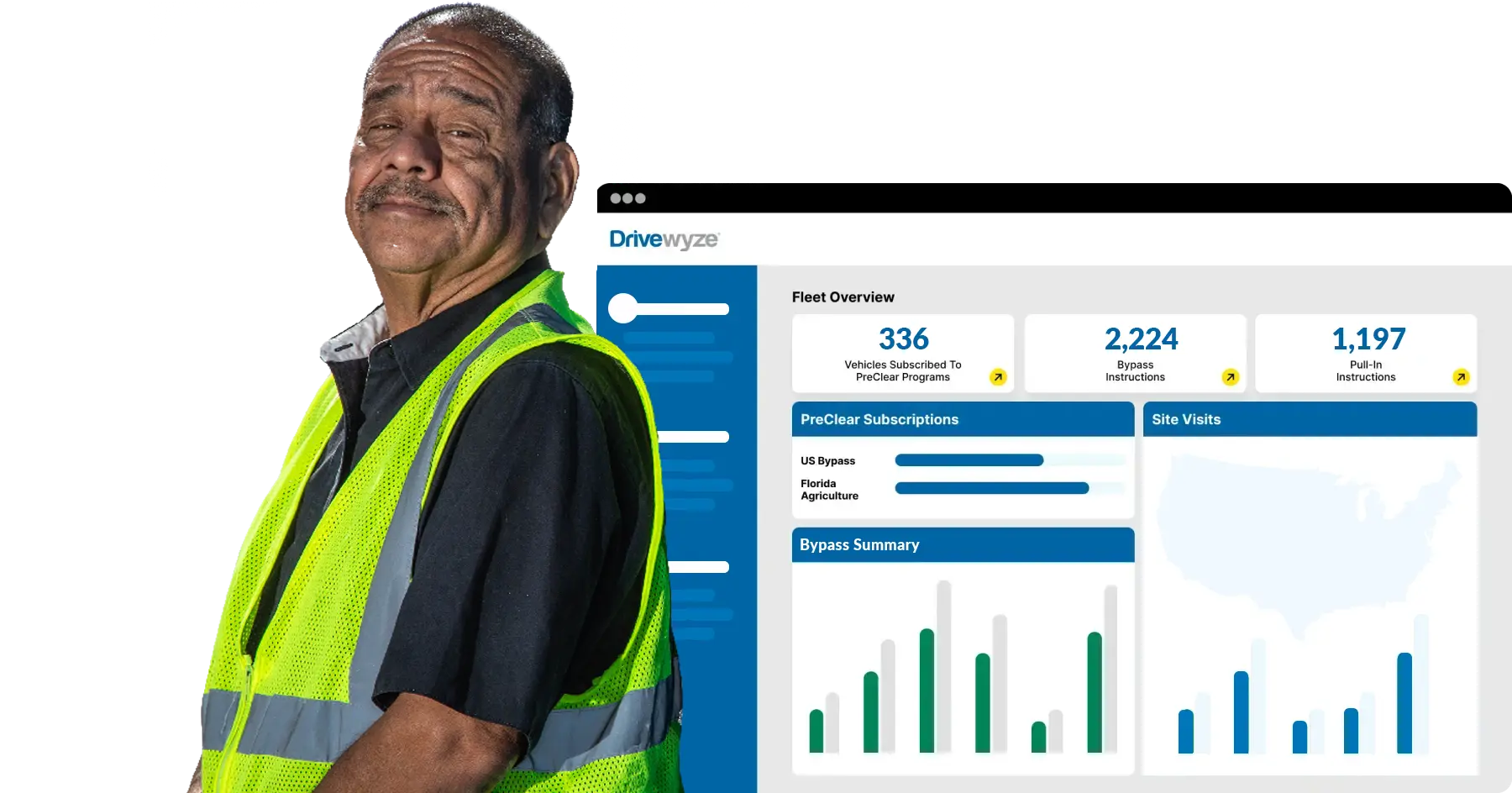
Generally, we’re not in the business of saying which is best. However, you should select an ELD device based on reliability, ease of use, additional features, and how well it integrates with other technology your fleet uses. Currently, Drivewyze integrates with more than 2.5 million ELD devices across the nation.
In case you’re curious about the best ELD devices on the market or pricing, Drivewyze partners with the following ELD providers:
- DriverTech
- Eleos
- FleetHunt
- Geotab
- Motive (Formerly KeepTruckin)
- Samsara
- Pedigree Technologies
- ISAAC
- ORBCOMM
- Omnitracs
- Platform Science
- Switchboard
- Rand McNally
- Transflo
- Trimble
- And more
Drivewyze – Protect Your Truckers And Your Bottom Line
Regardless of your ELD device, Drivewyze can help your fleet save a lot of time and money. Our fleet solutions easily integrate with most ELD devices on the market. Check out our services below:
Drivewyze works on most in-cab devices, including ELDs, mobile phones, and tablets, with no additional hardware required. Get started today.

Ready to Get Started?
Learn how Drivewyze can improve commercial transportation safety and efficiency